When developing with PHP, security must be a top priority. Poorly written code can expose your application to threats like SQL Injection, XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), and CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery). This guide walks through essential techniques and secure coding practices with practical examples.
1. Validate and Sanitize User Input
Never trust input from users. Always validate and sanitize before processing it.
✅ Secure Input Handling Example:
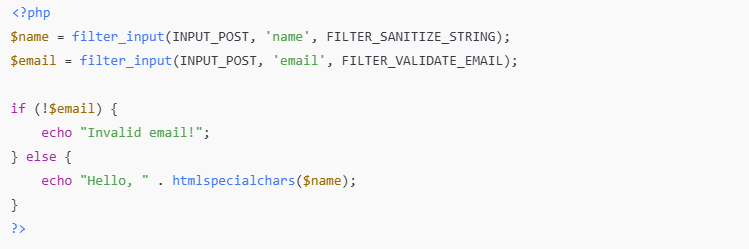
FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING: Removes potentially harmful characters.FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL: Ensures a valid email format.htmlspecialchars(): Escapes HTML to prevent XSS.
2. Prevent SQL Injection with Prepared Statements
Avoid inserting user input directly into SQL queries.
❌ Vulnerable Example:

✅ Secure Example:
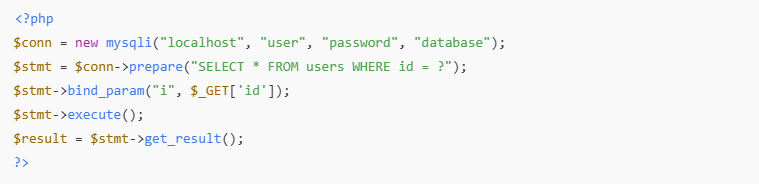
bind_param()safely binds values and enforces type ("i"for integer).- Prevents malicious manipulation of SQL logic.
3. Hash and Verify Passwords Properly
Never store passwords in plain text. Use built-in hashing functions.
✅ Storing a Hashed Password:
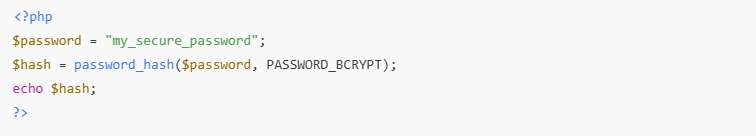
✅ Verifying on Login:

password_hash()uses a strong, salted algorithm.password_verify()checks input against the hash securely.
4. Escape Output to Prevent XSS
XSS occurs when attackers inject malicious scripts into your output.
✅ Example:

Without escaping, input like <script>alert('XSS')</script> would execute as code.
5. Protect Forms Against CSRF
Use tokens to ensure requests originate from trusted sources.
✅ CSRF Token Implementation:

- Tokens validate request legitimacy.
hash_equals()prevents timing attacks.
6. Hide Errors in Production
Displaying errors can reveal sensitive data. Disable error display and log them instead.
✅ php.ini Configuration:

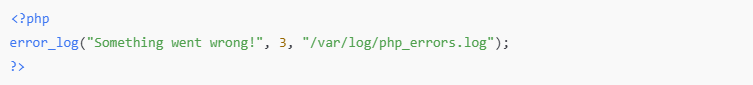
✅ Manual Logging Example:
7. Secure File Uploads
Allow only specific file types and validate uploads.
✅ File Type Validation:

- Store uploads outside public directories.
- Rename files and avoid executing them directly.
8. Disable PHP Execution in Upload Directories
Prevent attackers from uploading and running PHP files.
✅ .htaccess Example:

9. Add Security Headers
Use HTTP headers to add an extra layer of protection.
✅ Header Configuration:

Securing a PHP application requires attention to detail and consistent best practices. By validating inputs, using secure database access, protecting against XSS and CSRF, handling passwords properly, and configuring your environment securely, you can greatly reduce risk.
Build secure PHP apps—your users depend on it 🚀

